2251. Number of Flowers in Full Bloom
2251. Number of Flowers in Full Bloom
1 | You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array flowers, where flowers[i] = [starti, endi] means the ith flower will be in |
1
2
3
4
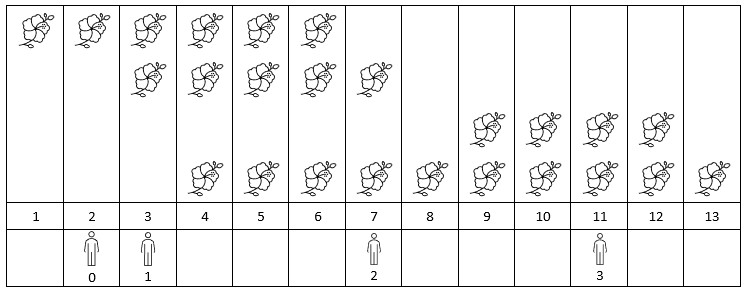
5Input: flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], persons = [2,3,7,11]
Output: [1,2,2,2]
Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive.
For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival.
Example 2: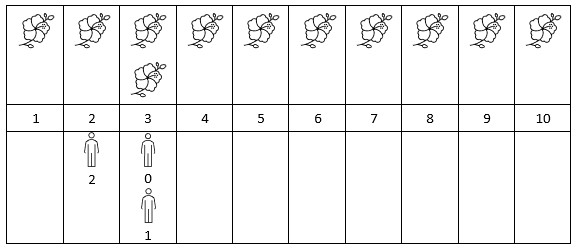
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13Input: flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], persons = [3,3,2]
Output: [2,2,1]
Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive.
For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival.
Constraints:
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104
flowers[i].length == 2
1 <= starti <= endi <= 109
1 <= persons.length <= 5 * 104
1 <= persons[i] <= 109
Difficulty : Hard
Solution
Prefix sum + binary search
1 | class Solution { |